KNOWLEDGE
Latest Article
CATEGORY
High-Pressure Pump Knowledge
15.Mar.2025
Types of Plunger Pumps: Get to Know Everything about Plunger Pumps - From Basic Principles to Structure
There are many types of industrial pumps, which can generally be divided into two main categories based on their working principles. The first category, known as dynamic pumps, uses rotational force—similar to a fan—to push liquids. The second category, positive displacement pumps, functions like a hand pump, displacing a fixed amount of liquid with each cycle. Understanding these two classifications is the first step in learning about different types of pumps.
In this article, we will explore the major and subcategories of pumps, with a particular focus on plunger pumps.
Unlike dynamic pumps, positive displacement pumps operate like a sealed chamber, delivering a fixed volume of liquid per cycle regardless of the liquid’s pressure or viscosity. This ensures a steady flow and makes them ideal for handling high-viscosity fluids or applications requiring high pressure.
Positive displacement pumps are mainly divided into two categories: rotary pumps and reciprocating pumps.
A plunger pump works similarly to a hand pump, using one or more plungers that move back and forth to push the liquid forward. As the plunger moves within the cylinder, it creates a suction and discharge cycle—first drawing liquid into the chamber, then forcefully expelling it.
Plunger pumps can handle both liquid and gas compression and are highly effective in applications requiring high-pressure fluid transfer. They maintain a stable flow even under extreme pressures and can efficiently handle viscous liquids or those containing solid particles.
A typical plunger pump consists of several key components:
Plunger pumps can be categorized in various ways based on their design and operating mechanisms. Below are some of the most common classifications.。
Each type of plunger pump serves a unique purpose in various scenario, depending on factors such as required pressure, flow rate, and fluid characteristics.
Selecting the best type of plunger pump depends on the specific operating conditions and fluid requirements. For instance, manufacturers specializing in triplex plunger pumps design them for high-pressure, low-flow applications, making them ideal for industrial cleaning and high-pressure washing systems.
Understanding these classifications ensures that you choose the right plunger pump for your industry, whether it be hydraulics, chemical processing, or wastewater treatment.
In this article, we will explore the major and subcategories of pumps, with a particular focus on plunger pumps.
Plunger Pumps: A Type of Reciprocating and Positive Displacement Pump
Unlike dynamic pumps, positive displacement pumps operate like a sealed chamber, delivering a fixed volume of liquid per cycle regardless of the liquid’s pressure or viscosity. This ensures a steady flow and makes them ideal for handling high-viscosity fluids or applications requiring high pressure.
Positive displacement pumps are mainly divided into two categories: rotary pumps and reciprocating pumps.
- Rotary pumps include gear pumps, lobe pumps, screw pumps, and peristaltic pumps.
- Reciprocating pumps include plunger pumps and diaphragm pumps.
Working Principle and Structure of Plunger Pumps
A plunger pump works similarly to a hand pump, using one or more plungers that move back and forth to push the liquid forward. As the plunger moves within the cylinder, it creates a suction and discharge cycle—first drawing liquid into the chamber, then forcefully expelling it.
Plunger pumps can handle both liquid and gas compression and are highly effective in applications requiring high-pressure fluid transfer. They maintain a stable flow even under extreme pressures and can efficiently handle viscous liquids or those containing solid particles.
A typical plunger pump consists of several key components:
- Plunger: The primary moving part that slides back and forth within the cylinder.
- Cylinder: The chamber where the plunger operates.
- Inlet and Outlet Valves:These act as check valves, allowing liquid to flow in one direction while preventing backflow.
- Connecting Rod and Crankshaft: Common in many designs, these components convert rotational motion into the reciprocating movement of the plunger.
- Plunger Pumps: Feature a stationary seal while the plunger moves through it, making them better suited for high-pressure applications and handling challenging fluid environments.
- Piston Pumps: Have seals attached to the piston, allowing for higher flow rates but with lower pressure capabilities compared to plunger pumps.
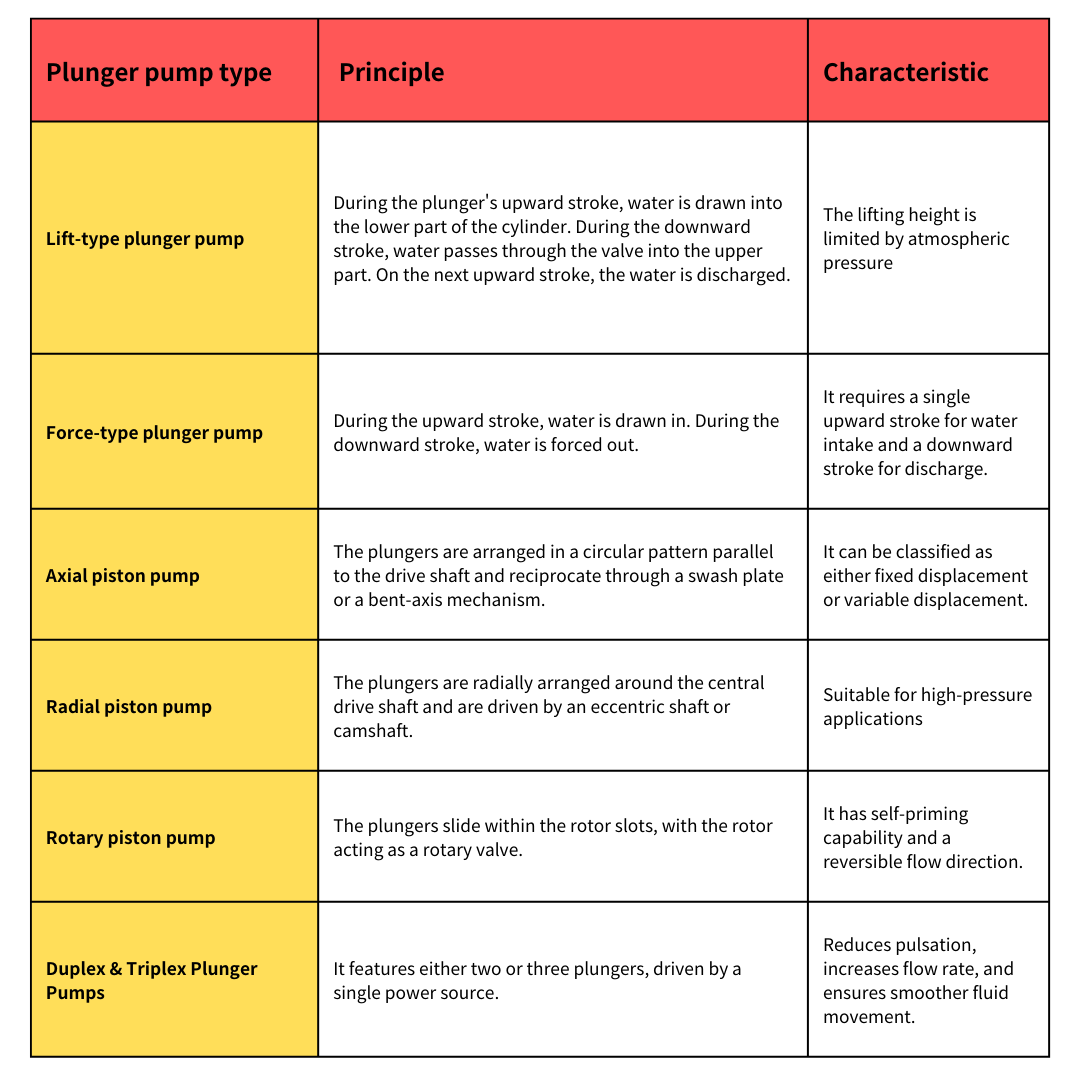
Types of Plunger Pumps and Their Classification Methods
Plunger pumps can be categorized in various ways based on their design and operating mechanisms. Below are some of the most common classifications.。
Basic Classification: Lift Piston Pumps vs. Force Piston Pumps
-
Lift Piston Pumps
This type functions similarly to traditional hand-operated water wells.
- During the upstroke, water is drawn into the lower chamber through a valve.
- During the downstroke, water passes through the plunger valve into the upper chamber.
- On the next upstroke, the water is expelled through the discharge outlet.
-
Force Piston Pumps
This design resembles a bicycle pump.
- During the upstroke, air or liquid is drawn into the cylinder through the inlet valve..
- During the downstroke, the fluid is pushed through the outlet valve with force.
- Single-acting pumps: Only discharge fluid during the downstroke.
- Double-acting pumps: Expel fluid during both up and down strokes, increasing efficiency.
Specialized Plunger Pump Designs
- Axial Plunger Pumps (Axial Piston Pumps)
- A swash plate or bent axis mechanism creates the reciprocating motion.
- Axial plunger pumps can be either fixed displacement (delivering a constant fluid volume) or variable displacement (adjustable flow rate by changing the swash plate angle).
- Radial Plunger Pumps (Radial Piston Pumps)
- Movement is controlled by an eccentric shaft or cam mechanism, generating a powerful pumping action.
- These pumps excel in ultra-high-pressure applications.
- Rotary Plunger Pumps (Rotary Piston Pumps)
- The rotor acts as a rotating valve, ensuring a continuous pumping cycle.
- These pumps typically have self-priming capabilities and can reverse fluid flow when needed.
-
Rotary Plunger Pumps (Rotary Piston Pumps)
- The rotor acts as a rotating valve, ensuring a continuous pumping cycle.
- These pumps typically have self-priming capabilities and can reverse fluid flow when needed.
Classification by Cylinder Count: Duplex & Triplex Plunger Pumps
- Duplex Plunger Pumps: Feature two plungers operating in tandem.
- Triplex Plunger Pumps: Utilize three plungers, providing smoother flow with reduced pulsation and increased efficiency.

Applications of Different Types of Plunger Pumps
Each type of plunger pump serves a unique purpose in various scenario, depending on factors such as required pressure, flow rate, and fluid characteristics.
- Axial and radial plunger pumps: Commonly used in high-pressure hydraulic systems.
- Rotary plunger pumps: Ideal for viscous fluid transfer.
- Duplex and triplex plunger pumps: Suited for applications requiring steady flow and high-pressure output.
Choosing the Right Plunger Pump for Your Application
Selecting the best type of plunger pump depends on the specific operating conditions and fluid requirements. For instance, manufacturers specializing in triplex plunger pumps design them for high-pressure, low-flow applications, making them ideal for industrial cleaning and high-pressure washing systems.
Understanding these classifications ensures that you choose the right plunger pump for your industry, whether it be hydraulics, chemical processing, or wastewater treatment.


